Will AI Replace Data Analysts?
Data analysis helps people understand their business and make informed decisions to improve it. Now that AI (especially large language models, a.k.a. LLMs) can reason, learn, write code, and complete tasks, it can help with data analysis. This article will explain:
- Why data analysis is important.
- Whether AI can replace a data analyst.
- How people already use AI for data analysis.
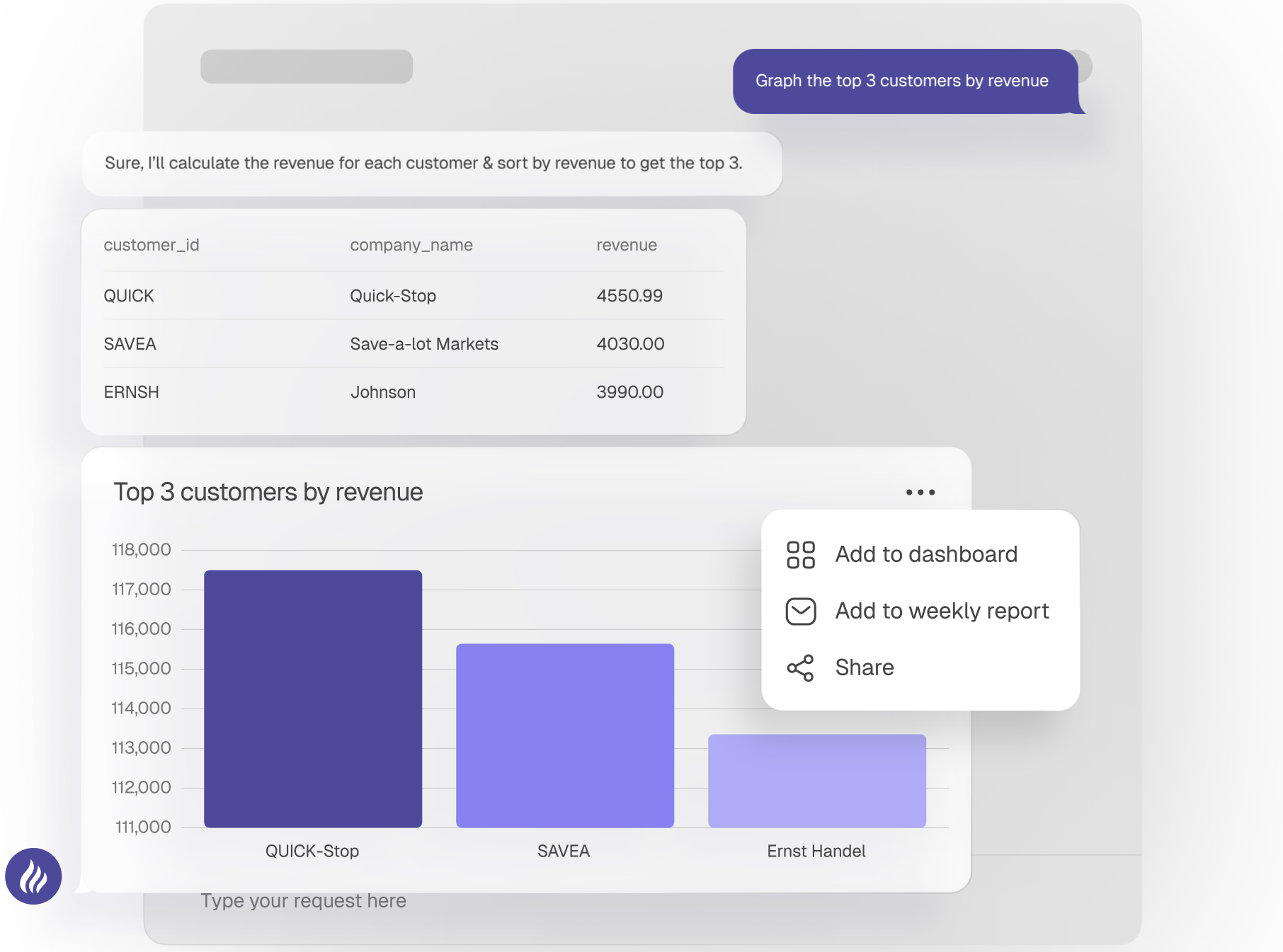
Why is data analysis so important?
Data analysis helps us understand what's actually happening. You need to understand what's actually happening if you want to improve things.
"Intensive users of customer analytics are 23 times more likely to clearly outperform their competitors in terms of new- customer acquisition than non-intensive users, and nine times more likely to surpass them in customer loyalty ... the likelihood of achieving above-average profitability is almost 19 times higher" - McKinsey
"Highly data-driven organizations are three times more likely to report significant improvements in decision-making compared to those who rely less on data." - Harvard Business Review
"You want to setup your culture so that the most junior person can overrule the most senior person if they have data." - Jeff Bezos, Founder of Amazon

Being data-informed makes it much easier to succeed. That's why we rely on data for important things like:
- Testing new medicines to see if they're safe and effective
- Predicting dangerous storms so people can prepare
- Analyzing economic trends to inform policy decisions (like interest rates)
That's also why people across all company functions rely on data analysis, including:
- Executives
- Sales & Marketing
- Product management
- Operations & Supply Chain
- Finance
- Human Resources
Why do people want to use AI for Data Analysis?
Data analysis skills are a bottleneck for insights
Almost everyone needs data insights, but most people don’t have the skills needed to get them. This means they depend on data analysts (or often developers and other technical staff). If you need someone's help to get insights, they often become a bottleneck for those insights. This slows you down, slows them down, and often prevents you from being data driven.
If people without data analysis skills can use AI for data analysis, there's no bottleneck.
Data analysts are expensive
Hiring employees (including data analysts) is expensive. On top of the monthly salary, you also have to consider recruiting, training, and other costs. This is especially problematic for small companies, or companies requiring many data analysts.
If AI is good enough at a job, it is a much cheaper alternative than hiring someone.
People with data analysis skills work faster with AI
Data analysts, and people with data analysis skills, can work faster with AI. It can generate code and complete other tasks that take time and effort. This allows data analysts and other technical staff to work faster.
Will AI Replace Data Analysts?
To answer this question, we will go through these main tasks of a data analyst to see if AI can complete them:
- Understanding the business or industry
- Data collection & preparation (incl. quality control)
- Data Analysis
- Reporting (incl. presenting)
We will classify AI's ability to complete these tasks using the following categories:
AI Capability - Given the current level of AI, is it technically capable of completing the task?
- Fully capable
- Mostly capable, with some human oversight
- Partially capable, requiring significant human input
- Not capable
*AI refers to the models (LLMs), not the analytics software that uses these LLMs. Their full potential is only realized when integrated with appropriate software and logic systems. It's important to distinguish between AI models themselves and the analytics software that utilizes these models. Even if a consumer-facing AI application like ChatGPT struggles with a particular task, it doesn't necessarily mean the underlying AI model (e.g., GPT-4) is incapable of that task. Specialized software can often leverage the same AI models more effectively, overcoming limitations seen in general-purpose chatbots.
Software Availability - Is there already AI Software that can be used to complete this task?
- Software exists
- Software doesn't exist yet
Let's go through the tasks of a data analyst, and whether AI can complete them.
1. Understanding the business or industry
Analysis without the right background knowledge is like solving a puzzle without the picture. To analyze data, you first need to understand the meaning of the data. To understand the industry and the company, it's essential for a data analyst to:
- Learn about the industry
- Learn about the company from documentation, reports, etc.
- Learn about the company from co-workers
AI Capability
Classification: 2. Mostly capable, with some human oversight
- Learn about the industry
- Various AI Models learn from datasets consisting of trillions of words. These datasets include information about many industries. This means these models often have more industry knowledge than junior data analysts.
- Learn about the company from documentation, reports, etc.
- Some AI models can fit over 1000 pages of information. Claude-3.5-Sonnet, the best model for data analysis tasks, can fit around 300 pages.
- Learn about the company from co-workers
- Since AI models can fit so many pages of information, they can also learn from co-workers.
- The main problem is that humans are better at remembering important information. AI Models are not great at evaluating how well they understand something, so humans need to fill knowledge gaps they notice.
Software availability
Classification: Software Exists
Several tools allow you to provide knowledge to AI assistants. For example:
- Microsoft Copilot Studio allows you to connect several knowledge sources.
- BlazeSQL extracts column descriptions from your database, and enables you to teach your AI about your company & database.
- ChatGPT allows you to provide knowledge to custom GPTs.
- Zenlytic has a semantic layer to provide this background knowledge via YAML files.
Future outlook
Classification: 1. Fully capable
At the current rate of improvement, AI that is capable of this task could exist within the next 5 years. There is already AI software that does this relatively well. Since both the software and the AI are consistently improving, they should be fully capable within 5 years.
Summary
- Current Capability: 2. Mostly capable
- Software Availability: Software exists
- Future Outlook: 1. Fully capable
2. Data Collection & Preparation
Some data analysts might work with a clean, high-quality database, but many others don't. It is common for data analysts to spend most of their time collecting and preparing data. This process can include:
- Gathering data from various sources and stakeholders.
- Data cleaning and quality assurance. This means making sure the data is accurate by:
- Checking basic statistics (like totals and averages) with people who know the business
- Making sure the data looks realistic in general
AI Capability
Classification: 3. Partially Capable, requiring a significant amount of human input
- Gathering data from various systems and stakeholders.
- People can create software that uses AI to browse file systems and request data from stakeholders.
- Unfortunately AI might not be able to interact with some old legacy software. Another issue is the difficulty in dealing with uncooperative or unresponsive stakeholders.
- Data cleaning and quality assurance. This means making sure the data is correct by:
- Checking basic statistics (ex. totals and averages) with people who can roughly verify them.
- AI can generate code to calculate these statistics and interpret the results. It could then send these to stakeholders for verification.
- Again, dealing with unresponsive or uncooperative stakeholders may be an issue.
- Making sure the data looks realistic in general
- Quality assurance and exploratory data analysis are common tasks. Training data for models like GPT-4 includes many examples of this kind of analysis. This means they are generally capable of this.
- Checking basic statistics (ex. totals and averages) with people who can roughly verify them.
Software availability
Classification: Software doesn't exist yet
Existing AI software can generate code for quality assurance, and support with preparation. But validating the results with stakeholders is an important part of this process. Currently, no AI software supports reaching out to stakeholders for validation.
Future outlook
Classification: 1. Mostly Capable
AI that is mostly capable of this task could exist within the next 5 years. The main issue is that dealing with stakeholders sometimes requires a human touch (soft skills).
Summary
- Current Capability: 3. Partially Capable
- Software Availability: Software Doesn't exist yet
- Future Outlook: 2. Mostly Capable
3. Data Analysis
This is the task most people think of when they think of a data analyst’s role. it includes:
- Extracting & transforming data from databases & files (SQL, NoSQL, csv, excel, etc.)
- Exploratory data analysis, statistical analysis, and interpreting results.
- Creating visualizations & Dashboards
- Getting feedback & guidance from colleagues (ex. subject matter experts) throughout the analysis
AI Capability
Classification: 2. Mostly Capable, with some human oversight.
- Extracting & transforming data from databases & files (SQL, NoSQL, csv, excel, etc.)
- This task mostly consists of writing code. AI Models like Claude-3.5-Sonnet have exceptional coding capabilities. They can extract & transform data based on requests made in natural language. Most companies should be able to leverage AI for this if the data structure is clean and not too complex.
- Providing background knowledge about the database and company is sometimes necessary during setup.
- Exploratory data analysis, statistical analysis, and interpreting results.
- As with extraction & transformation, AI uses its coding ability here. As the majority of analysis tends to be simple (given a somewhat clean data source), AI usually succeeds.
- For the interpretation of more complex analysis, AI generated interpretations may be unreliable. It's best to have AI present the results (the data & graphs), for humans to interpret.
- Creating visualizations & Dashboards
- In the majority of cases (most graphs tend to be quite simple) this is already possible.
- Getting feedback & guidance from colleagues (ex. subject matter experts) throughout the analysis
- Many AI applications are conversational, meaning humans go back and forth with AI. AI can learn throughout this conversation and receive feedback. If a subject matter expert is dealing with AI, they can guide it and provide feedback as needed.
Software availability
Classification: Software exists
Existing AI analytics software can generate extract, transform, analyze and visualize data. This is often done in a chat, which allows AI to get feedback from the user in the chat.
- Julius AI is an AI Data Analyst for csv files and other smaller files
- ChatGPT runs python code on uploaded files via the “advanced data analysis” feature
- BlazeSQL connects to your SQL Database, to run queries and visualize results
Future outlook
Classification: 2. Mostly Capable
It's not clear that LLMs will overcome all their numeric reasoning weaknesses in the next 5 years. It's also not clear whether they will be able to deal with messy or overly complex databases. This means reliable interpretation and handling certain data sources may remain a limitation.
With a clean data source, AI can do the majority of analysis if a human interprets the results.
Summary
- Current Capability: 2. Mostly Capable
- Software Availability: Software Exists
- Future Outlook: 2. Mostly Capable
4. Reporting
The point of data analysis is getting insights for better decision making. Communicating those insights to the relevant people is the purpose of this last task. This may come in the form of a presentation, an email, a document, or various other options. This task can include:
- Consolidating results in a report or presentation
- Presenting results to stakeholders & answering questions
- Doing extra analysis based on stakeholder feedback or questions
AI Capability
Classification: 2. Mostly Capable, with some human oversight.
- Consolidating results in a report or presentation
- As discussed in the previous sections, AI can extract and visualize data. Since it can also generate natural language, it can be used to generate reports.
- Natural language interpretations may not be reliable in more complex cases.
- Presenting results to stakeholders & answering questions
- Live presentations are possible for AI, but humans will perform better. Ex. If someone looks confused or skeptical, a human will be better at noticing and addressing it. Building trust is also a key element that AI would struggle with here.
- Doing extra analysis based on stakeholder feedback or questions
- This is essentially the same as task 3 (data analysis), which AI is mostly capable of.
Software availability
Classification: Software doesn’t exist yet (partially)
There is software that enables AI generated reports and sends them to stakeholders. There is no Software that supports live AI-driven presentations of data analysis. Since most ongoing reporting isn't a presentation, AI software can often handle it.
Future outlook
Classification: 2. Mostly Capable
It's unlikely that AI will be able to interact with groups and build trust as humans do any time soon. As mentioned in the future outlook of task 3, the same goes for numeric reasoning. Analysis, interpretation and building trust via presentations will remain a struggle.
Most reporting does not happen in the form of live presentations. Subject matter experts who receive these reports are usually able to interpret results, so AI is useful for reporting in most cases.
Summary
- Current Capability: 2. Mostly Capable
- Software Availability: Software Exists
- Future Outlook: 2. Mostly Capable
So, will AI replace data analysts?
We can’t say that AI will replace data analysts, at least not in all cases. For most of the tasks of a data analyst, parts of the task can be difficult to complete in some situations. That doesn't mean AI is not useful for data analysis. In fact, for certain data analysis work, AI is already used without a data analyst.
By understanding the abilities and limitations, we can use AI for successful data analysis. Some situations in which AI can be particularly useful:
- Non-technical staff with beginner-level technical knowledge can analyze data with AI. They may have enough understanding to provide the necessary oversight. Directly working with the data via AI may be faster and more effective than depending on a data analyst.
- Companies without data teams often depend on developers for data insights. This is often slow, ineffective, and slows down their development work. Using AI Tools is not the same as hiring a data analyst, but it can often be the best thing in these situations. This is often true in these cases:
- The data is in a clean and well-structured database.
- There is not enough work to keep a full-time data analyst busy.
- There is not enough budget to hire a data analyst.
- Most people who need insights have basic technical knowledge.
- Data Analysts themselves (or others with data analysis skills) can use AI as an assistant. This allows them to work faster and automate a lot of their work.
The following companies already use AI for data analysis:
- DTC Pages uses AI for CRO. Here’s what their CRO Specialist had to say: “I use Julius AI to analyze and visualize data when doing research for CRO clients at DTC Pages.“
- Lola sells physical and subscription based products directly to consumers. They needed to enable self-service data analysis to make their people more informed. Their VP of Direct-to-consumer said “I think having AI Analytics functionality has been really helpful in that I can just type in what I need without help. I start almost 80% of my queries with AI”
- Hoo.be is a link-in-bio tool (used by Jeff Bezos), and they use an AI Assistant to analyze their data. They have a lean team, and no data analysts. Here’s what their CTO had to say: “Blaze saves our team hours of manual work each week by automating the process of writing the queries we use to analyze our business. It unlocks a new level of analysis, filling in our SQL knowledge gaps and writing complex queries that enable us to dig deeper into our data than ever before.”
- Poppy.be is a car sharing company without a data team that uses AI to enable over 30% of their company to independently analyze data. Here’s what their CTO had to say: “Sometimes all you want is a quick answer from your data. That is the gap filled by BlazeSQL, and it saves our team lots of time.”
As AI and its applications continue to improve, we can expect deeper adoption and use of AI for increasingly complex data analysis tasks. However, the critical thinking, domain expertise, and stakeholder management skills of human data analysts will remain valuable in many companies.
While AI will significantly transform the field of data analysis, it won't replace data analysts entirely. The future of data analysis lies in the collaboration between humans and AI tools. By embracing this change and leveraging AI effectively, organizations can enhance their data analysis capabilities, leading to better insights and more informed decision-making.
This page will be regularly updated to reflect improvements in AI over the coming years.



